By Isabella Figueroa
In a new book, archeologists who study past societies of the Great Lakes and Midwest agree “you are what you eat,” but they say there’s a lot more to it than that. It’s also how we eat: the ways we “prepare, cook and consume” those foods are influenced by our history, family and natural environment.The book’s essays use the concept of cuisine to go beyond ingredients when studying thousand-year old foodways in regions that now make up Michigan, Indiana, Illinois, Wisconsin and other states.
Land
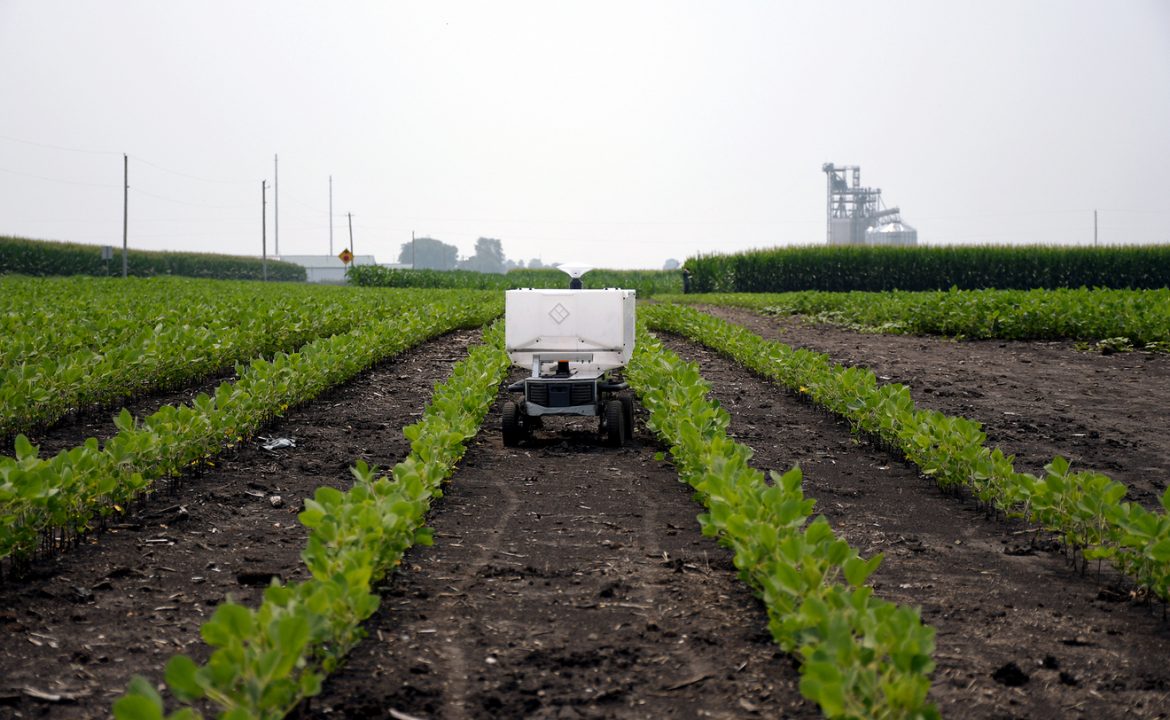
Tradition meets technology: Illinois report says future of farming includes AI and robots
|
By Shealyn Paulis
The future of farming might be more digital than you expect. Researchers say technology and artificial intelligence could be the answer to future agriculture resilience and sustainability.
Land
In debate over protecting large or small natural areas, answer may be both
|
By Ruth Thornton
A new study finds that large, continuous natural areas protect more plants and animals than many small patches, but small patches also provide valuable biodiversity benefits. The UP has more large areas than the Northern Lower Peninsula.
Land
‘Forest-to-table’: Rural, Indigenous communities rely on forests for food, medicine and cultural values, research shows
|
By Victoria Witke
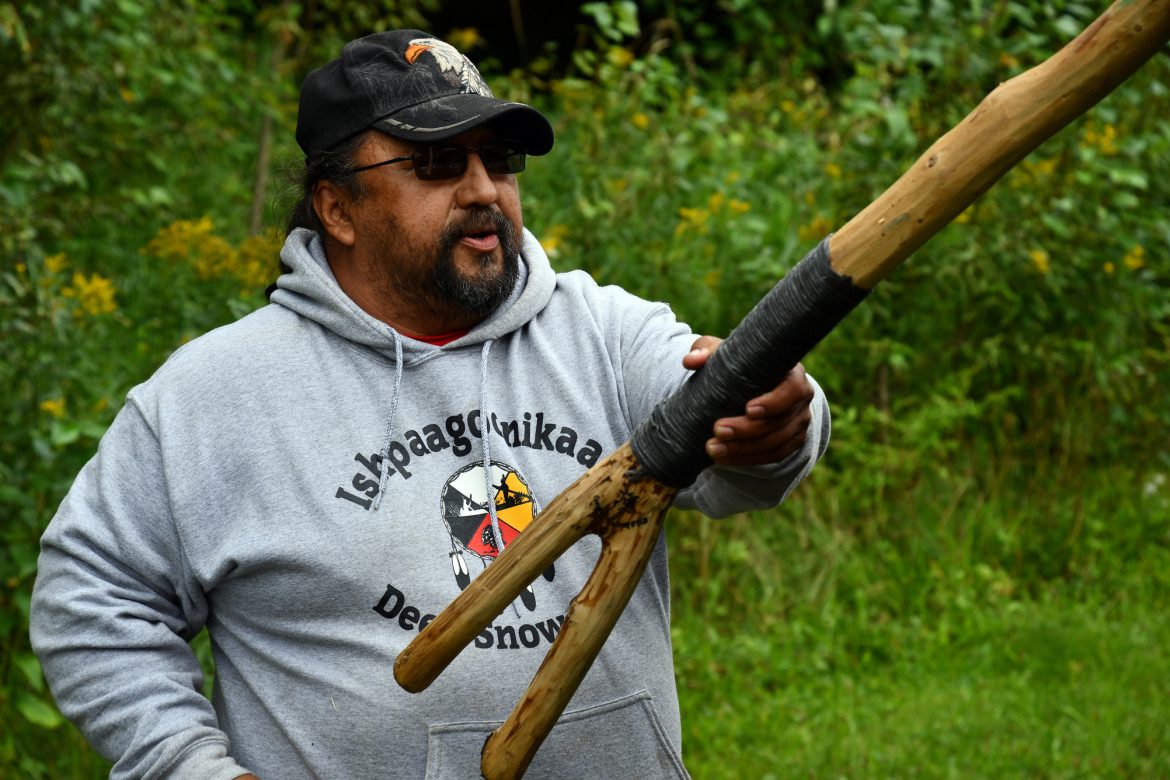
When Roger LaBine was younger, he often drove his grandfather to the Ottawa National Forest to hunt porcupines for food and more, including birch bark-and quill baskets He’s a member of the Lac Vieux Desert Band of Lake Superior Chippewa Indians. A notable proportion of the population relies on public forests for food, and Michigan ranked third in a new study in the amount of wild meat hunted on public lands.
Land
Lawmakers consider new rules for pet cemeteries
|
By Finn Mills
here’s a proposal from a West Bloomfield senator to tighten state regulation of pet cemeteries, sparked in part by problems with a Howell pet cemetery that shut down in 2018, leaving pet owners to exhume the remains of their departeds.
Echo
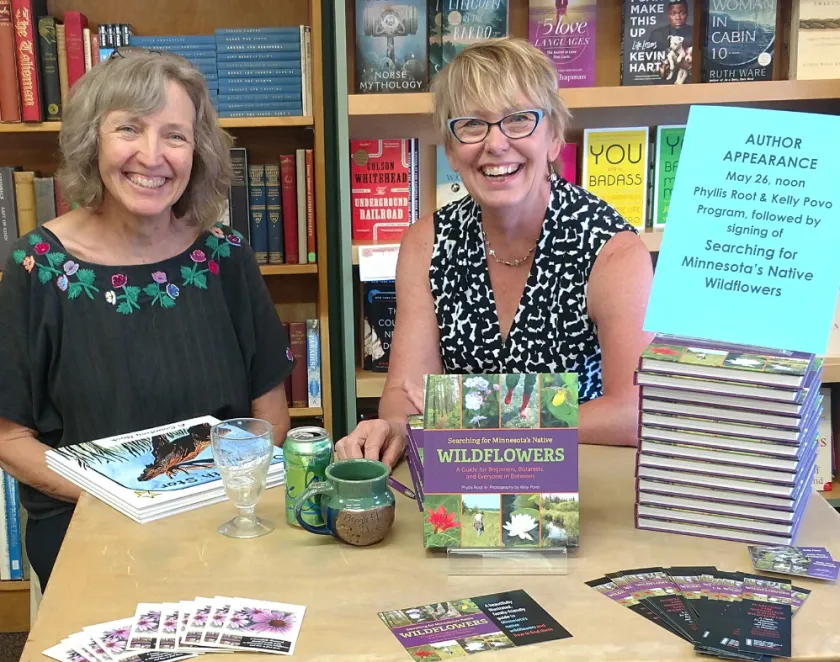
Putting passion to pages: Minnesota authors release second guide to state wildflowers
|
By Shealyn Paulis
Two Minnesota nature enthusiasts have spent years chasing the state’s most elusive wildflowers. Their journey, filled with adventure and discovery, is now captured in their upcoming book, Chasing Wildflowers: An Adventurous Guide to Finding Minnesota’s Native Flowers in Their Unique Habitats.
Land
Forever chemicals in biosolids may pose problems for municipalities, farmers
|
By Ruth Thornton
A common practice by farmers to fertilize their fields may be spreading forever chemicals into new areas and into the food supply. It can be a cost-effective way for municipalities to dispose of sewage sludge but raises health concerns.
Land
Cover crop mixes can cut carbon emissions from farms, study says
|
By Victoria Witke
A new U-M study done in Lenawee, Tuscola and Monroe counties finds that cover crop mixtures on farms can help mitigate adverse impacts of climate change, instead of single species cover crops. There are concerns about the freezing of federal payments for agriculture programs.
Land
Legislation to increase land division could expand housing opportunities, but worries arise
|
By Daniel Schoenherr
A new Senate bill would make it easier to subdivide parcels of 10 or more acres in what proponents say would encourage construction of more affordable housing. Critics counter it could put a strain on municipal infrastructure. Sponsor is from St. Clair Shores.
Climate
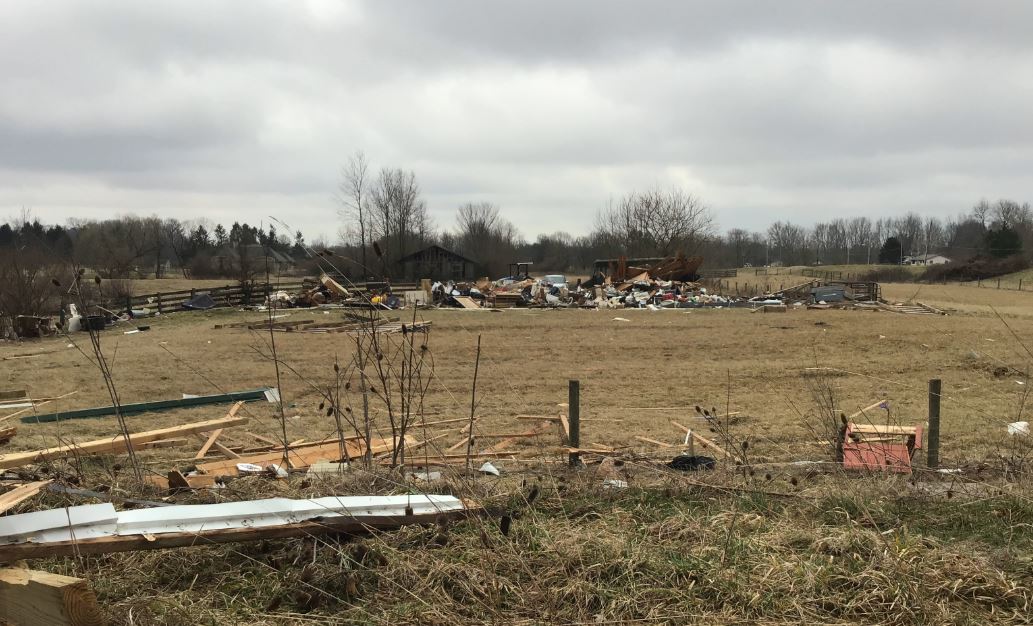
Many elderly Ohioans feel unprepared for severe weather, study finds
|
By Clara Lincolnhol
Ohio took a beating from a record-breaking 73 tornadoes in 2024. Twisters and other severe weather events are becoming more common in the Midwest due to climate change, and seniors are more at risk. As the threat from major storms grows, roughly one in five older adults living in central Ohio say they feel unprepared or uncertain of their readiness for a severe weather event, according to a recent study conducted by The Ohio State University. The study surveyed more than 1,400 individuals aged 65 and older living in eight counties to gauge their preparedness for a severe weather event. Questions were based on storm-readiness recommendations from the Federal Emergency Management Agency.
Overall, 78% of participants said they felt prepared for severe weather, 13% said they did not and 9% felt unsure.
The study also asked individuals if severe weather caused them significant life disruptions, such as preventing them from getting to doctor’s appointments or from accessing medication or other vital supplies.
Land
New strategies driving public lands acquisitions
|
By Gabriel S. Martinez
Capital News Service
The Michigan Department of Natural Resources is looking for deals to create more green space in populated areas as part of an updated public lands strategy. The goal is to equitably provide public access to green space, wildlife habitat and public hunting closer to where people live, department officials say. Efforts in the past two years include acquisitions in Van Buren, Monroe and Ionia counties.
Those involved buying private land adjacent to public land to consolidate green spaces.
Scott Whitcomb, the director of the DNR’s Office of Public Lands, said a major pending deal involving Black River Ranch in Sanilac County is expected to close by the end of 2025. That property acquisition will bring in about 8,844 acres, including over 14 miles of the Black River, the East Branch of the Black River, Stewart Creek and three lakes including 150-acre Silver Lake. It will become part of the Pigeon River Country Forest Management Unit.