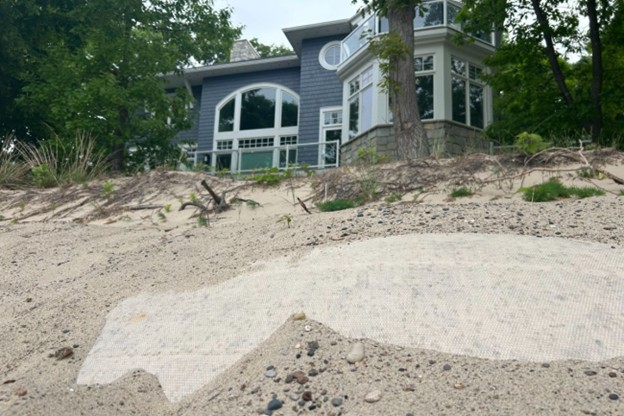

By Emilio Perez Ibarguen
In 2020, Lawmakers gathered testimony, sought federal funding and considered creating a task force to combat coastal erosion. Local governments looked to replace outdated zoning rules that let people build too close to the shore. Experts suggested fixes, from incentivizing property owners to move their homes farther inland to banning seawalls that ultimately worsen erosion. But the political will for change seemed to recede with the water. Five years since the height of the crisis — with water levels now 6 inches below average — most Michigan communities still allow home construction perilously close to the shore. Bills aiming to curb construction on coastal dunes or make it easier for homeowners to protect their homes with temporary barriers have failed to gain traction in the Legislature.

By Rachel Lewis
After the great “moose lifts” in the 1980s, researchers were confident Michigan’s moose population would continue to grow, with a projection that the population could reach numbers in the thousands within 15 years. However, since 2010, the DNR has seen the moose population growth stagnate, with population estimates half of what was expected after the reintroduction. This prompted a collaboration among researchers to look into what’s causing the lack of population growth.
By Rachel Lewis
Boxwood shrubs are popular in Michigan because they add greenery in winter months and deer don’t eat them. They had no predators until 2021, when the box tree moth was discovered in New York. Quarantine areas have grown from 11 to 13 counties in Michigan over the last two years.

By Emilio Perez Ibarguen
Homeowners and environmental groups are pushing for reforms to restrict
wake boats to deeper areas far from shore, aligning Michigan law with existing guidance from the
Department of Natural Resources. A handful of states including Maine, Vermont and Tennessee in recent years have passed laws limiting wakeboarding to specific areas or deeper waters, while a push to do so in Michigan last year was dead in the water in Lansing. Wake boat enthusiasts say they’re being scapegoated for a larger problem.
More Headlines




